Suggested Videos
Part 42 - ASP.NET Core model validation | Text | Slides
Part 43 - Select list validation in asp.net core | Text | Slides
Part 44 - AddSingleton vs AddScoped vs AddTransient | Text | Slides
This is an introduction to Entity Framework Core. Entity Framework Core, also called EF Core is a complete rewrite from the ground up. If you have any experience with previous versions of Entity Framework, you will find lot of familiar features.
What is EF Core
EF Core is an ORM (Object-Relational Mapper).
EF core is lightweight, extensible, and open source software. Like .NET Core, EF Core is also cross platform. It works on windows, Mac OS, and Linux. EF core is Microsoft’s official data access platform.
What is ORM
ORM stands for Object-Relational Mapper and it enables developers to work with a database using business objects. As a developer we work with the application business objects and the ORM generates the SQL that the underlying database understands. In-short, an ORM, eliminates the need for most of the data-access code that developers usually need to write.
Why use an ORM
Let's understand, the use of an ORM with an example. If we are developing an application to manage employees we would have classes like Employee, Department etc in our application code. These classes are called the Domain classes.
Without an ORM like EF Core, we have to write a lot of custom data access code to store and retrieve employee and department data from the underlying database.
For example to read, insert, update or delete data from the underlying database table we have to write code in the application to generate the required sql statements that the underlying database understands. Also when the data is read from the database into our application, we again have to write custom code to map the database data to our model classes like Employee, Department etc. This is a very common task that we do almost in every application.
An ORM like EF Core can do all of this for us and saves a lot of time. It sits between our application code and the Database. It eliminates the need for most of the custom data-access code that we usually have to write without an ORM.
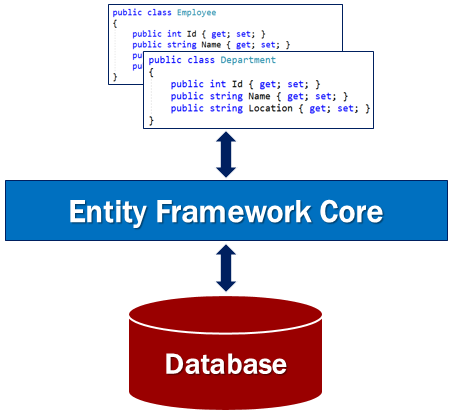
EF Core Code First Approach
EF Core supports both Code First approach and Database First approach. However, with the Database First approach there is very limited support in EF core at the moment.

With the Code First Approach, we first create our application domain classes like Employee, Customer etc and a special class that derives from Entity Framework DbContext class. Based on these domain and DBContext classes, EF Core creates the database and relevant tables. Out of the box, EF Core uses it's default conventions to create the database and database tables. You can change these default conventions if you want to.
EF Core Database First Approach

Sometimes we may have an existing database. When we have a database and the database tables already, we use the database first approach. With the database first approach, EF Core creates the DBContext and Domain classes based on the existing database schema.
EF Core Database Providers
EF Core supports many relational and even non relational databases. EF Core is able to do this by using plug-in libraries called the database providers. These database providers are available as NuGet packages.

List of EF Core Database Providers
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ef/core/providers/
A database provider, usually sits between EF Core and the database it supports. The database provider contains the functionality specific to the database it supports. Functionality that is common to all the databases is in the EF Core component. Functionality that is specific to a database, for example, Microsoft SQL Server specific functionality is with-in the SQL Server provider for EF Core.
We will discuss more about this provider model when we include support for SQL server in our asp.net core application in our upcoming videos.

Part 42 - ASP.NET Core model validation | Text | Slides
Part 43 - Select list validation in asp.net core | Text | Slides
Part 44 - AddSingleton vs AddScoped vs AddTransient | Text | Slides
This is an introduction to Entity Framework Core. Entity Framework Core, also called EF Core is a complete rewrite from the ground up. If you have any experience with previous versions of Entity Framework, you will find lot of familiar features.
What is EF Core
EF Core is an ORM (Object-Relational Mapper).
EF core is lightweight, extensible, and open source software. Like .NET Core, EF Core is also cross platform. It works on windows, Mac OS, and Linux. EF core is Microsoft’s official data access platform.
What is ORM
ORM stands for Object-Relational Mapper and it enables developers to work with a database using business objects. As a developer we work with the application business objects and the ORM generates the SQL that the underlying database understands. In-short, an ORM, eliminates the need for most of the data-access code that developers usually need to write.
Why use an ORM
Let's understand, the use of an ORM with an example. If we are developing an application to manage employees we would have classes like Employee, Department etc in our application code. These classes are called the Domain classes.
Without an ORM like EF Core, we have to write a lot of custom data access code to store and retrieve employee and department data from the underlying database.
For example to read, insert, update or delete data from the underlying database table we have to write code in the application to generate the required sql statements that the underlying database understands. Also when the data is read from the database into our application, we again have to write custom code to map the database data to our model classes like Employee, Department etc. This is a very common task that we do almost in every application.
An ORM like EF Core can do all of this for us and saves a lot of time. It sits between our application code and the Database. It eliminates the need for most of the custom data-access code that we usually have to write without an ORM.

EF Core Code First Approach
EF Core supports both Code First approach and Database First approach. However, with the Database First approach there is very limited support in EF core at the moment.

With the Code First Approach, we first create our application domain classes like Employee, Customer etc and a special class that derives from Entity Framework DbContext class. Based on these domain and DBContext classes, EF Core creates the database and relevant tables. Out of the box, EF Core uses it's default conventions to create the database and database tables. You can change these default conventions if you want to.
EF Core Database First Approach

Sometimes we may have an existing database. When we have a database and the database tables already, we use the database first approach. With the database first approach, EF Core creates the DBContext and Domain classes based on the existing database schema.
EF Core Database Providers
EF Core supports many relational and even non relational databases. EF Core is able to do this by using plug-in libraries called the database providers. These database providers are available as NuGet packages.

List of EF Core Database Providers
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ef/core/providers/
A database provider, usually sits between EF Core and the database it supports. The database provider contains the functionality specific to the database it supports. Functionality that is common to all the databases is in the EF Core component. Functionality that is specific to a database, for example, Microsoft SQL Server specific functionality is with-in the SQL Server provider for EF Core.
We will discuss more about this provider model when we include support for SQL server in our asp.net core application in our upcoming videos.

No comments:
Post a Comment
It would be great if you can help share these free resources